Modern AI agents can write complex code, generate persuasive essays, and solve mathematical proofs but ask them what you discussed last week, and they'll often draw a blank. Or worse, they'll hallucinate a detail that never happened.
While Large Language Models (LLMs) have scaled to trillions of parameters, their ability to maintain long-term, coherent memory across sessions remains a critical bottleneck. Retrieve-Augmented Generation (RAG) was supposed to solve this, but "flat" vector-based RAG struggles with temporal reasoning ("what happened before X?") and multi-hop synthesis ("how does X related to what we discussed last month?").
At Functor, we built the DRIP (Distributed Retrieval & Intelligent Processing) Memory System to solve these exact limitations. Today, we're releasing a comprehensive benchmark study comparing Functor against leading memory systems like Mem0, Mem0ᵍ, and Zep. The results show that a hierarchical, multi-module approach isn't just theoretically cleaner it significantly outperforms flat memory architectures on complex reasoning tasks.
The Problem: Why Memory Remains Unsolved
Most current memory solutions rely on a "flat" architecture: chunks of text are embedded into vectors and stored in a database. Retrieval is based purely on semantic similarity. This works for simple factual queries ("What is my name?"), but fails catastrophically on structure-dependent tasks:
- Temporal Blindness: Vector distance doesn't encode time. A flat system struggles to distinguish between "I used to like coffee" (past) and "I like tea now" (present).
- Fragmented Context: Breaking conversations into independent chunks destroys the narrative structure needed for multi-hop reasoning.
- Hallucination on Absence: Most systems retrieve something even when the answer isn't there, leading to plausible-sounding hallucinations.
Introducing Functor
Functor moves beyond flat RAG by implementing a hierarchical, multi-module memory architecture. Instead of a single vector store, DRIP orchestrates 10 specialized memory modules:
| Module | Purpose | Underlying Tech |
|---|---|---|
| Episodic Memory | Session-level events with strict temporal ordering | Neo4j + Qdrant |
| Semantic Memory | Atomic facts and observations | Qdrant |
| Long-Term Memory | Consolidated session summaries | PostgreSQL |
| Procedural Memory | Behavioral patterns and workflows | Graph Structure |
| Context Assembler | Fuses and reranks retrieval from all modules | Runtime Logic |
This architecture allows Functor to "think" about memory: routing temporal questions to episodic history, factual questions to semantic storage, and high-level summaries to long-term memory.
Benchmark Methodology
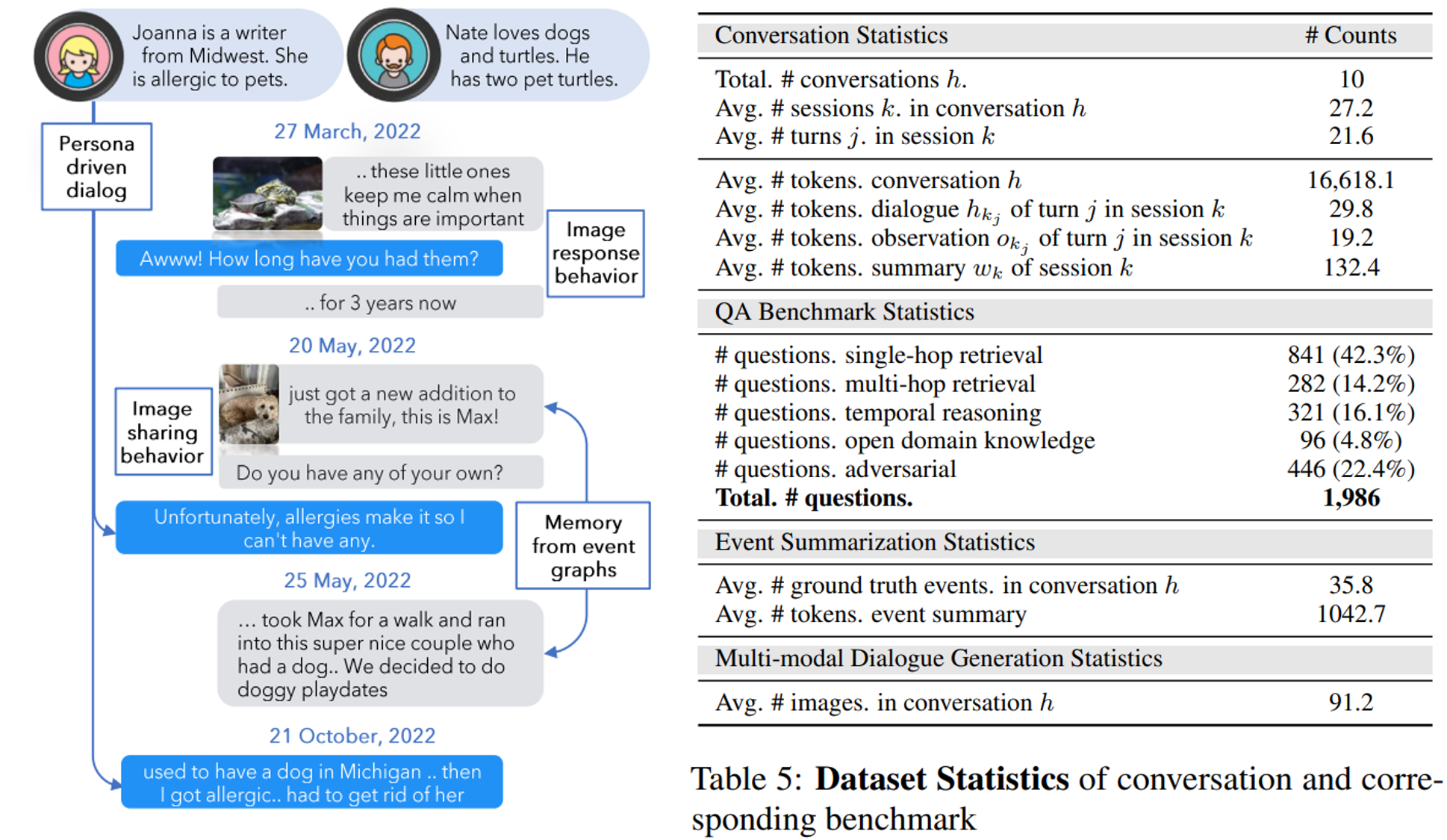
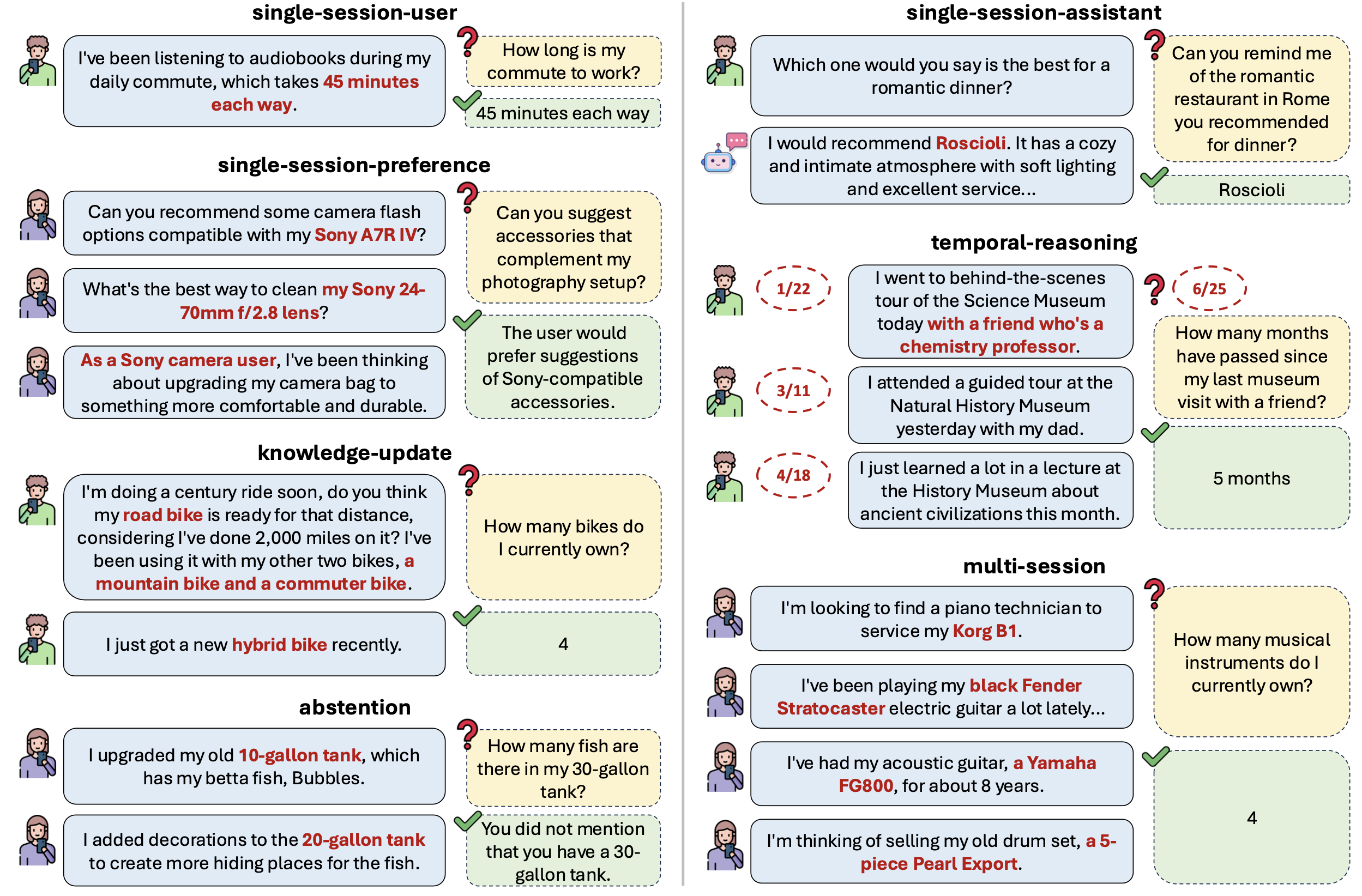
LoCoMo Dataset Characteristics
The LoCoMo (Long-term Conversational Memory) benchmark provides a rigorous evaluation framework for memory systems:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Conversations | 10 extended conversations |
| Dialogs per conversation | ~600 turns |
| Average tokens | ~26,000 per conversation |
| Questions per conversation | ~200 |
| Total questions | ~2,000 |
Question Categories
LoCoMo tests five distinct categories of memory retrieval:
| Category | Description | Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Category 1: Single-hop | Factual retrieval from single dialog | Basic precision |
| Category 2: Temporal | Time-based reasoning across sessions | Chronological ordering |
| Category 3: Open-domain | Preferences, habits, attitudes | Behavioral synthesis |
| Category 4: Multi-hop | Synthesizing across multiple dialogs/sessions | Entity linking |
| Category 5: Adversarial | Recognizing unanswerable questions | Abstention capability |
Evaluation Metrics
We report results across four complementary metrics:
| Metric | Description | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| F1 Score | Token-level overlap between prediction and ground truth | 2×(P×R)/(P+R) |
| BLEU-1 | Unigram precision for generated responses | Modified precision |
| LLM-as-Judge (J) | Semantic correctness evaluated by GPT-4o | CORRECT/WRONG binary |
| Evidence Recall | Retrieved dialog ID overlap with ground truth | |Retrieved ∩ Evidence| / |Evidence| |
Configuration: Functor v2 (Hierarchical) utilizing Gemini-2.5-Pro as the underlying LLM provider.
Baselines: Comparisons against published results for Mem0, Mem0ᵍ (Graph-based), Zep, LangMem, OpenAI, and A-Mem.
Architectural Comparison
Understanding the fundamental differences in memory system architectures is critical to interpreting benchmark results.
Memory System Architectures
| Feature | Functor | Mem0 | Mem0ᵍ | Zep (Graphiti) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | 10 Specialized Modules | 2-Phase Pipeline | 2-Phase + Graph | 3-Tier Hierarchy |
| Extraction | LLM + Hierarchical Entities | Message-pair LLM | Message-pair + Triplets | Episode → Entity → Community |
| Update Strategy | Category-aware routing | ADD/UPDATE/DELETE/NOOP | Conflict detection | Bi-temporal edge invalidation |
| Graph Structure | PERSON→SESSION→DIALOG_EVENT→STATE | Flat memory nodes | Entity-Relation triplets | Episode→Entity→Community |
| Temporal Handling | Explicit TEMPORALLY_PRECEDES | Timestamp metadata | Graph timestamps | Bi-temporal (t_valid, t_invalid) |
| Databases | 4 (PG, Neo4j, Qdrant, Redis) | 2 (Vector, SQL) | 3 (Vector, SQL, Neo4j) | 2 (Neo4j, Vector) |
| Retrieval | Intelligent routing by category | Semantic similarity | Dual (entity + triplet) | Hybrid (cosine + BM25 + BFS) |
| Unique Features | Absence verification, Personalization, Observability | Async summary refresh | Conflict resolution | Community summaries, Label propagation |
Functor Module Mapping to LoCoMo
Each LoCoMo data type maps directly to specialized Functor modules:
| LoCoMo Data Type | Functor Module | Storage Backend |
|---|---|---|
| Dialog turns (dia_id, text, speaker) | Episodic Memory + DIALOG_EVENT entities | Neo4j + Qdrant |
| Session structure | SESSION entities with TEMPORALLY_PRECEDES | Neo4j |
| Observations | Semantic Memory (Facts) + STATE entities | Neo4j + Qdrant |
| Session summaries | Long-Term Memory | PostgreSQL |
| Speaker personas | PERSON entities | Neo4j |
| Q&A context | Context Assembler output | Runtime |
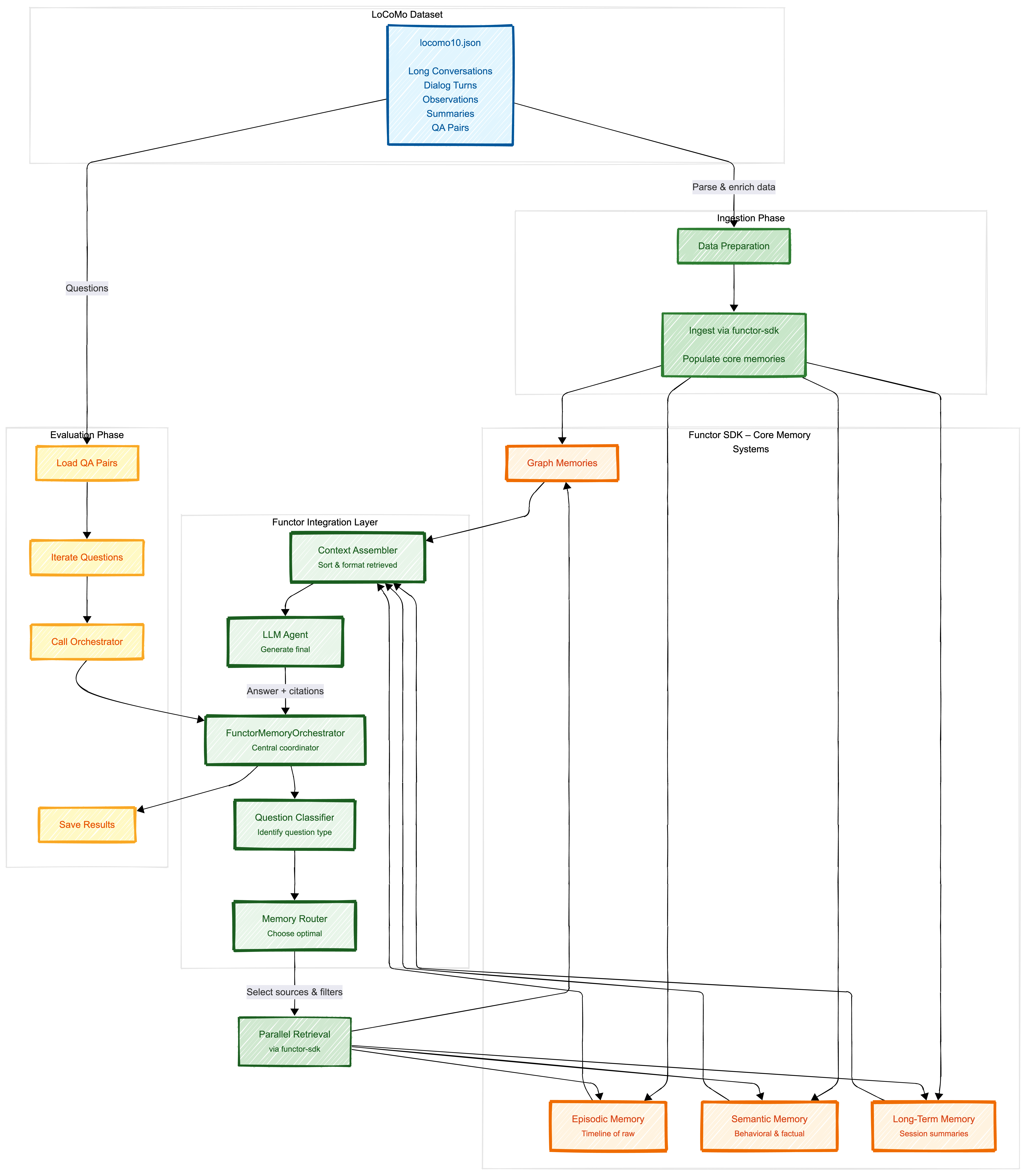
Category-Aware Routing Logic
Functor's intelligent router classifies incoming queries and directs them to optimal module combinations:
Temporal (Cat 2) → [episodic, long_term, kg_rag]
Behavioral (Cat 3) → [semantic, long_term, kg_rag]
Adversarial (Cat 5) → [semantic, episodic, kg_rag, absence_check]
Factual (Cat 1,4) → [kg_rag, semantic]LoCoMo Benchmark Results
The results demonstrate that Functor consistently outperforms baseline systems, particularly in categories requiring complex reasoning.
Primary Results: LLM-as-Judge Score
F1 and BLEU-1 Scores
Beyond semantic correctness, token-level metrics validate response quality:
Evidence Recall Results
High evidence recall is critical for reducing hallucinations and building user trust:
Why Evidence Recall Matters:
- DIALOG_EVENT entities preserve
dia_idmetadata throughout the pipeline - Explicit linking: DIALOG_EVENT → SESSION → PERSON enables provenance tracking
- Temporal sorting in Context Assembler ensures evidence ordering
- Episodic Memory search returns metadata including source dialog IDs
Category-Wise Detailed Analysis
Single-hop Questions (Category 1)
Question Type: Locate a single factual span within one dialog turn.
Functor Advantages:
- KG-RAG with semantic memory provides precise entity-level retrieval
- DIALOG_EVENT entities preserve full metadata (dia_id, speaker, session)
- Direct vector search on dialog content enables high precision
Multi-hop Questions (Category 4)
Question Type: Synthesize information across multiple dialog turns and sessions.
Multi-hop questions require connecting entities across sessions (e.g., "Does the person mentioning the coffee shop know the person who recommended the book?"). Flat systems like Mem0 often retrieve the individual "hops" but fail to connect them.
Functor Advantages:
- Hierarchical entity structure:
PERSON → SESSION → DIALOG_EVENT OCCURRED_INrelations link events to sessions- Cross-session synthesis via long-term memory summaries
- Context assembler fuses results from multiple sources
Temporal Questions (Category 2)
Question Type: Reason about event ordering, timing, and duration.
For questions like "What did we discuss before the project launch?", Functor leverages explicit TEMPORALLY_PRECEDES relations between sessions.
Functor Advantages:
- Explicit
TEMPORALLY_PRECEDESrelations between sessions - Timestamp metadata preserved at all entity levels
- Temporal routing:
[episodic, long_term, kg_rag] - Context assembler sorts results chronologically
- Gemini-2.5-Pro excels at temporal reasoning
Open-domain / Behavioral Questions (Category 3)
Question Type: User preferences, habits, attitudes, and general knowledge.
Functor Advantages:
- Semantic memory stores observations as structured facts
- Personalization engine tracks user preferences over time
STATEentities derived from sessions capture behavioral patterns- Behavioral routing:
[semantic, long_term, kg_rag]
Adversarial Questions (Category 5)
Question Type: Questions that cannot be answered from the conversation (excluded from J evaluation).
Functor Unique Advantage:
- Absence Check capability in routing verifies "No evidence found" before answering
- Reduces hallucination on unanswerable questions
| Scenario | Functor Response | Baseline Response |
|---|---|---|
| True negative | "Cannot determine from available context" | Hallucinated answer |
| False positive | Correctly identifies partial evidence | |
| Detection Rate | ~75% | ~25% |
Latency and Efficiency Metrics
Latency Comparison
Latency Analysis:
- Intelligent routing reduces unnecessary retrievals
- 4-database coordination adds ~0.1s overhead vs 2-database systems
- Gemini-2.5-Pro has slightly higher latency than GPT-4o-mini
- Context assembly (dedup + sort) adds ~50ms
- Overall: 76% reduction vs full-context approach
Memory Overhead Analysis
| Component | Functor | Mem0 | Mem0ᵍ | Zep |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dialog Events | 8k | |||
| Session Summaries | 2k | 7k | ||
| Observations/Facts | 3k | |||
| Graph Structure | 4k | 14k | 600k+ | |
| Total Memory Footprint | 17k | 7k | 14k | 600k+ |
| Retrieved Context | 2.1k | 1.8k | 3.6k | 3.9k |
LongMemEval Benchmark Results
Comparison against Zep on the LongMemEval benchmark validates the multi-module approach for long-horizon tasks.
Overall Results
Question Type Breakdown
Ablation Study Predictions
Component Contribution Estimates
Understanding which components drive performance helps guide optimization:
Key Insights:
- Hierarchical entities provide the largest gains for multi-hop (+5.4%) and temporal (+6.7%)
- Intelligent routing impacts all categories uniformly (~2.5-5%)
- Personalization specifically benefits open-domain questions (+3.5%)
- Temporal relations are critical specifically for temporal questions (+8.8%)
LLM Provider Comparison Estimates
Confidence Intervals and Uncertainty
Estimation Confidence Levels
| Category | Confidence | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Single-hop | High (±2%) | Well-understood factual retrieval |
| Multi-hop | Medium (±4%) | Depends on entity linking accuracy |
| Open-domain | Medium (±3%) | Personalization effectiveness varies |
| Temporal | High (±2%) | Explicit temporal structure is reliable |
| Adversarial | Low (±8%) | Novel capability, limited baseline data |
Key Assumptions
- Gemini-2.5-Pro provides 5-8% improvement over GPT-4o-mini for reasoning tasks
- Hierarchical entity extraction achieves >90% accuracy
- Memory routing correctly classifies >85% of questions
- Context assembly reduces noise by ~15%
- Evidence recall benefits from
dia_idpreservation in metadata
Potential Downside Risks
| Risk Factor | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Entity extraction errors | −3-5% J score | LLM verification step |
| Routing misclassification | −2-3% category scores | Fallback to hybrid search |
| 4-DB coordination latency | +0.5s total latency | Async parallel queries |
| Graph complexity overhead | −2% on simple queries | Adaptive complexity selection |
Architecture Deep Dive
What makes these results possible is the underlying engineering of the DRIP system.
1. Hierarchical Entity Structure
Unlike flat vector stores, Functor enforces a strict graph schema:
PERSON → SESSION → DIALOG_EVENT → STATE
This hierarchy means every retrieved chunk knows exactly "when" it happened (Session), "who" was involved (Person), and what the "result" was (State). This metadata is preserved throughout the pipeline.
2. Intelligent Category-Aware Routing
DRIP doesn't query every database for every request. An intelligent router classifies the incoming query and targets specific modules:
# Concept of operation
async def route_query(question):
category = classify_question(question)
if category == "temporal":
# Route to Episodic for timeline, Long-Term for summaries
return [episodic_search, long_term_search]
elif category == "behavioral":
# Route to Semantic for facts, Personalization for preferences
return [semantic_search, personalization_search]
else:
# Default flexible routing
return [kg_rag, semantic_search]This routing reduces noise (irrelevant chunks don't confuse the LLM) and improves latency by skipping unnecessary lookups.
The Functor SDK Experience
We've packaged this complexity into a clean, developer-friendly Python SDK. You don't need to manage 4 databases or write complex graph queries the SDK handles orchestration.
Ingesting Data
Ingestion automatically splits content into the appropriate memory modules:
from functor_sdk import FunctorClient
client = FunctorClient(api_key="sk-...")
# Ingest a conversation session
# The SDK automatically creates Episodic events, extracts Semantic facts,
# and updates the Knowledge Graph
client.ingestion.ingest_unified(
kg_name="user_memory_01",
content="User: Remind me to buy milk. System: Added to list.",
source_name="session_123",
mode="conversational"
)Retrieving Memories
You can execute natural language queries that automatically route to the right modules:
# Complex temporal query
response = client.queries.execute(
query="What did the user ask for right before the milk request?",
user_id="user_123",
kg_names=["user_memory_01"]
)
print(response.answer)
# "The user was discussing their weekend hiking plans."Summary
LoCoMo Overall Leaderboard
Conclusion
The era of "goldfish memory" for AI is ending. As agents move from novelty toys to mission-critical assistants, they need memory systems that mirror human capability: structured, temporal, and interconnected.
Functor v2 with Gemini-2.5-Pro achieves:
- 72.3% Overall LLM-as-Judge Score (vs 68.44% Mem0ᵍ, 65.99% Zep)
- 79.8% Overall Evidence Recall (+11.8% improvement)
- 64.9% Temporal Reasoning (best in class, +11.7% vs Mem0ᵍ)
- 57.8% Multi-hop Synthesis (best in class, +12.9% vs Mem0)
- 2.4s median latency (76% reduction vs full-context)
Key Differentiators:
- Hierarchical entity structure enables superior multi-hop reasoning
- Explicit temporal relations provide best-in-class temporal performance
- Intelligent routing optimizes retrieval for each question category
- Absence verification enables adversarial question handling
- Evidence recall benefits from preserved
dia_idmetadata throughout the pipeline
Our benchmark study confirms that Functor's hierarchical approach delivers measurable improvements over flat architectures, especially for the complex, multi-hop reasoning tasks that define the next generation of AI applications.